
| HOME | MITOSIS | MEIOSIS I | WORKCITED |
| KEY TERMS TO
KNOW: Very similar
to Mitosis, Meiosis II’s sister chromatids are
seprarted. At the end of Meiosis II,
four daughter cells are created. Each
cell is a haploid and cannot divide again until fertilization.
MEIOSIS II
The sister chromatids
separate and are move toward
opposite poles of
the cell by the spindle. The cell begins to lengthen towards the
poles.Prophase II
In the chromosome, the haploid cell come together, the spinde clings onto the kinetochore of each chromosome, the nuclear envelope falls away, and going toward the poles of the cell are the centrosomes. Metaphase II The chromosomes line up along the center of the metaphase plate, waiting for anaphase II. Anaphase II Telephase II The cell continues to lengthen
and the mitotic spindle deteriorates. A
new nuclear envelope forms at each end of the cell and the chromosomes
within may unfold into chromatin.
Cytokinese II Splitting up between the two haploids are the cytoplasm and organelles. At the completion of Cytokinese II, four genetically unlike cells are made. 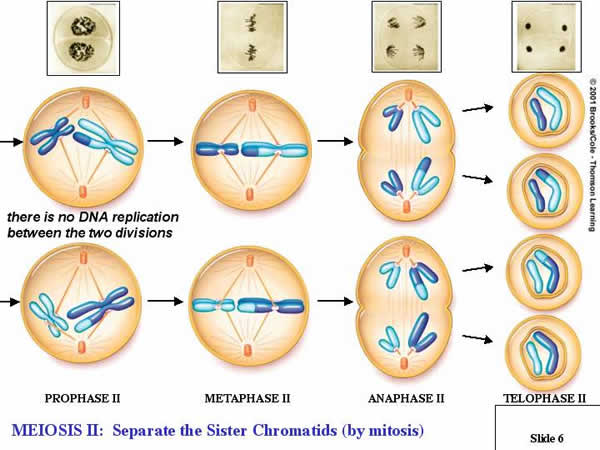 |
BACK TO TOP
LAST UPDATED:16 July 2009
© Copyright 2009 Raymond P. Dinh
E-MAIL ME